Convert German Money To Usd
first trading day
| year | $=DM |
| 1971 | 3.643 |
| 1972 | 3.273 |
| 1973 | 3.205 |
| 1974 | 2.758 |
| 1975 | 2.418 |
| 1976 | 2.619 |
| 1977 | 2.346 |
| 1978 | 2.071 |
| 1979 | 1.822 |
| 1980 | 1.713 |
| 1981 | 1.975 |
| 1982 | 2.242 |
| 1983 | 2.374 |
| 1984 | 2.761 |
| 1985 | 3.173 |
| 1986 | 2.438 |
| 1987 | 1.918 |
| 1988 | 1.585 |
| 1989 | 1.764 |
| 1990 | 1.709 |
| 1991 | 1.490 |
| 1992 | 1.528 |
| 1993 | 1.637 |
| 1994 | 1.742 |
| 1995 | 1.554 |
| 1996 | 1.435 |
| 1997 | 1.541 |
| 1998 | 1.789 |
| 1999 | 1.655 |
The 1971-2005 data in this left-hand table are from Triacom, a translation services company in Barendorf, Germany.
They generated it from oanda.com; see: Daily Rates section, below.
The discrepancy with the eh.net table on the right is because the left-hand table has first trade date of the year values, while the right-hand table has annual averages. If a year's value in the right-hand table is higher, then the year average dollar rate was stronger than at the start of the year (said another way: the DM got weaker that year).
Lawrence H. Officer, Professor of Economics at the University of Illinois at Chicago, on his InfoEurope page:
"From 1913 onward, all the European series are annual averages of daily exchange rates in the New York market."
Prof. Officer also gives the following details about German currency names:
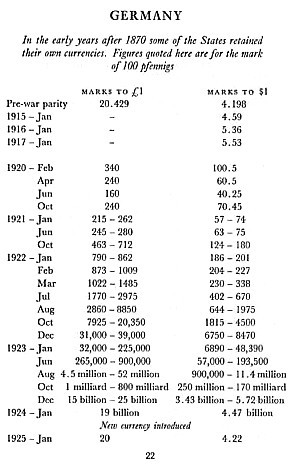
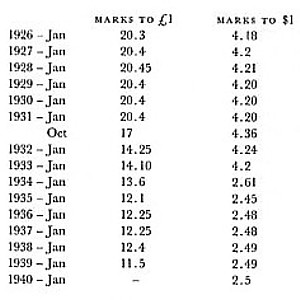
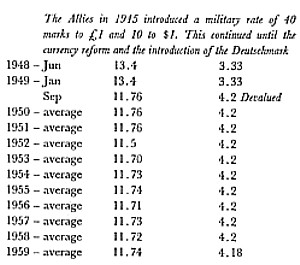
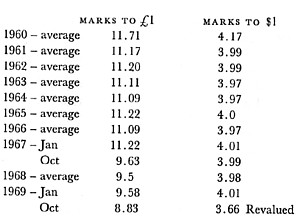
"On October 11, 1924 the monetary unit of Germany was changed from the mark to the reichsmark, where 1 reichsmark = 1,000,000,000,000 mark. Federal Reserve quotations switched from the mark to the reichsmark on October 29, 1924. In June 1948 the monetary unit was changed to the deutsche mark, where 1 deutsche mark = 10 reichsmark."
| Originally from: http://eh.net/hmit/ | |
| year | $1=Marks, annual avg. |
| 1913 | M 4.20 |
| 1914 | M 4.23 |
| 1915 | M 4.85 |
| 1916 | M 5.50 |
| 1917 | M 5.77 |
| 1918 | N/A |
| 1919 | M 32.85 |
| 1920 | M 57.11 |
| 1921 | M 83.02 |
| 1922 | M 430.48 |
note on Bidwell at left:
British milliard=US billion, British billion=US trillion.
| 1923 | M 50,000.00 |
| 1924 | M 4,329,000,000. |
| 1925 | RM 4.20 |
| 1926 | RM 4.20 |
| 1927 | RM 4.21 |
| 1928 | RM 4.19 |
| 1929 | RM 4.20 |
| 1930 | RM 4.19 |
| 1931 | RM 4.23 |
| 1932 | RM 4.21 |
| 1933 | RM 3.28 |
| 1934 | RM 2.54 |
| 1935 | RM 2.48 |
| 1936 | RM 2.48 |
| 1937 | RM 2.49 |
| 1938 | RM 2.49 |
| 1939 | RM 2.50 |
| 1940 | RM 2.50 |
| 1941 | RM 2.50 |
| 1942-1949 | not available |
| 1950 | DM 4.20 |
| 1951 | DM 4.20 |
| 1952 | DM 4.20 |
| 1953 | DM 4.20 |
| 1954 | DM 4.20 |
| 1955 | DM 4.21 |
| 1956 | DM 4.20 |
| 1957 | DM 4.20 |
| 1958 | DM 4.19 |
| 1959 | DM 4.18 |
| 1960 | DM 4.17 |
| 1961 | DM 4.02 |
| 1962 | DM 4.00 |
| 1963 | DM 3.99 |
| 1964 | DM 3.98 |
| 1965 | DM 3.99 |
| 1966 | DM 4.00 |
| 1967 | DM 3.99 |
| 1968 | DM 3.99 |
| 1969 | DM 3.92 |
annual averages
| Source still: | |
| 1970 | DM 3.65 |
| 1971 | DM 3.48 |
| 1972 | DM 3.19 |
| 1973 | DM 2.65 |
| 1974 | DM 2.58 |
| 1975 | DM 2.46 |
| 1976 | DM 2.52 |
| 1977 | DM 2.32 |
| 1978 | DM 2.00 |
| 1979 | DM 1.83 |
| 1980 | DM 1.82 |
| 1981 | DM 2.26 |
| 1982 | DM 2.43 |
| 1983 | DM 2.55 |
| 1984 | DM 2.85 |
| 1985 | DM 2.94 |
| 1986 | DM 2.17 |
| 1987 | DM 1.80 |
| 1988 | DM 1.76 |
| 1989 | DM 1.88 |
| 1990 | DM 1.62 |
| 1991 | DM 1.66 |
| 1992 | DM 1.56 |
| 1993 | DM 1.66 |
| 1994 | DM 1.62 |
| 1995 | DM 1.43 |
| 1996 | DM 1.50 |
| 1997 | DM 1.74 |
| 1998 | DM 1.76 |
| 1999 | DM 2.08 |
Links (back to top)
- CPI-based inflation calculator, from 1800 to present for US $ (westegg.com)
- The Consumer Price Index is good for comparing goods in daily use (salaries, food).
- created by Steven Morgan Friedman, a 1998 history major from UPenn, who became an excellent programmer-web designer (Friedman's CV).
- US Gov't CPI table, 1913-present, indexed 1982-84=100 (for US cities); monthly+annual avg.
- The same 1913-present table, but with annual averages, and annual percentages
- 1800-present table of annual averages, with 1967=100
- Inflation calculator, 1913-present, for US $, by US gov't Bureau of Labor & Statistics
- NASA's inflation calculator page (for US $, 1940 to 2009), includes links to:
- a CPI index running from 1913 to 2003.The CPI index is best for consumer goods.
- a GDP Deflator Inflation Calculator, which is better for industrial goods and construction projects.
- for a discussion comparing CPI, GDP and other measures see this page at measuringworth.com.
- The CPI is, of course, most accurate for consumer goods.
- For additional historical currency links, see this H-German e-mail exchange, Aug. 2005, which includes the following table:
- Implicit GNP Deflator 1913=100 (Germany, 1901-1995, gap 1914-1924)
Table based on one submitted by Prof. Albrecht Ritschl (Humboldt University, Berlin.), who used the source: Albrecht Ritschl and Mark Spoerer,: "Das Bruttosozialprodukt in Deutschland nach den amtlichen Volkseinkommens- und Sozialproduktsstatistiken 1901-1995," in: Jahrbuch fuer Wirtschaftsgeschichte (1997), part 2, 11-37. The article title translates as: "Gross National Product in Germany based on the Official National Income and Product Statistics, 1901-1995."1901 87.3
1902 86.2
1903 86.0
1904 85.9
1905 89.9
1906 92.2
1907 93.1
1908 91.3
1909 93.5
1910 96.5
1911 96.8
1912 99.3
1913 100.0
1914 n.a.
1915 n.a.
1916 n.a.1917 n.a.
1918 n.a.
1919 n.a.
1920 n.a.
1921 n.a.
1922 n.a.
1923 n.a.
1924 n.a.
1925 140.9
1926 144.2
1927 147.3
1928 152.8
1929 155.7
1930 154.9
1931 146.1
1932 131.6
1933 125.3
1934 126.4
1935 125.6
1936 125.1
1937 126.0
1938 128.1
1939 130.1
1940 125.8
1941 120.1
1942 118.4
1943 120.2
1944 126.5
1945 n.a.
1946 161.4
1947 171.6
1948 198.51948 198.5
1949 211.6
1950 204.8
1951 229.3
1952 240.4
1953 237.9
1954 237.5
1955 242.5
1956 249.3
1957 256.5
1958 264.5
1959 268.9
1960 276.8
1961 290.4
1962 302.0
1963 311.51964 321.1
1965 333.1
1966 344.5
1967 349.8
1968 357.7
1969 372.7
1970 401.2
1971 432.4
1972 455.4
1973 484.0
1974 517.9
1975 548.0
1976 567.7
1977 589.0
1978 614.0
1979 638.01980 669.3
1981 696.7
1982 727.7
1983 752.8
1984 768.5
1985 785.4
1986 811.3
1987 827.0
1988 837.1
1989 857.4
1990 884.6
1991 919.1
1992 969.2
1993 1,005.8
1994 1,029.1
1995 1,051.8 - Roy Davies, University of Exeter librarian, has a Current Value of Old Money page, with links to On-line tools & sources (they start with the eh.net site I used, above [note 2008: the eh.net site has become measuringworth.com]).
- Pounds to Dollars Historical Conversion of Currency by Eric Nye, Department of English, University of Wyoming (source years: 1264-1983; target years 1913-2007)
- French Franc-to-Euro consumer price index equivalencies, 1901-2001, in English, from the French Institut National de la Statistique et des Études Économiques: www.insee.fr.
- from 2002: Euro-to-Euro CPI
- pre-1800 German currency, at hudsonrivervalley.net (with conversion rates at the bottom of the page) and 1632.org/1632Slush/1632money.rtf:
The thaler (from thal, "valley") originally came from the coins minted from the silver from a rich mine at Joachimsthal (St. Joachim's Valley, Czech: Jáchymov) in Bohemia. Thalers/dollars were thus silver coins, while Guilders or Florins were gold (florin: name of gold coin minted in Florence in 1252). Here are some equivalencies (dear god, thank you for the decimal system)
1 Karolin = 11 rhenish florins
1 Dukaten = 5 fl rhein. (since 1559)
1 Laubtaler = 2 fl 45 Kreuzer rhein.
1 Königstaler = 1 fl 20 Kreuzer rhein.
1 Reichsthaler = 1.5 fl rhein. = 24 groschen = (theoretically) 12 pfennigs
(depended on copper vs. silver supply; latter became scarce during 30 years war, 1618-1648)
1 gulden = 4 mark = 24 albus = 48 schilling = 288 heller; 1 Gulden = 1 Guilder (Dutch)
1 groschen = 1 shilling (?)
or:
1 fl rhein. = 15 Batzen = 20 Groschen = 60 Kreuzer = 240 Denar (Pfennig) = 480 Heller
1 Albus = 1 1/2 Batzen = 2 Groschen = 6 Kreuzer = 24 Denar = 48 Heller
1 Batzen = 4 Kreuzer = 16 Denar = 32 Heller
1 Groschen = 3 Kreuzer = 12 Denar = 24 Heller
1 Kreuzer = 4 Denar = 8 Heller
1 Denar = 2 Heller
2006: 7,846 page views; 6,967 entry - 6,679 exit=288 ( 21.5/day)
2007: 14,989 page views; 13,753 entry - 13,419 exit=334 ( 41.1/day)
2008: 25,839 page views; 23,682 entry - 23,184 exit=498 ( 70.8/day)
2009: 31,917 page views; 29,858 entry - 29,215 exit=643 ( 87.4/day)
2010: 48,320 page views; 45,444 entry - 44,996 exit=448 (132.4/day)
2011: 55,713 page views; 52,917 entry - 52,459 exit=458 (152.6/day)
2012: 65,076 page views; 62,101 entry - 61,129 exit=972 (177.8/day)
2013: 54,077 page views; 51,679 entry-50,871 exit=808 (148.2/day)
2014: 34,387 page views; 32,603 entry-31,446 exit=1,157 (94.2/day)
2015: 55,075 page views; 51,694 entry-51,374 exit=320 (150.9/day)
2016: 85,579 page views; 71,814 entry-71,432 exit=382 (233.8/day)
2017: 90,941 page views; 86,543 entry-86,209 exit=334 (249.2/day)
2018:
Convert German Money To Usd
Source: https://marcuse.faculty.history.ucsb.edu/projects/currency.htm
Posted by: gaglianothise1989.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Convert German Money To Usd"
Post a Comment